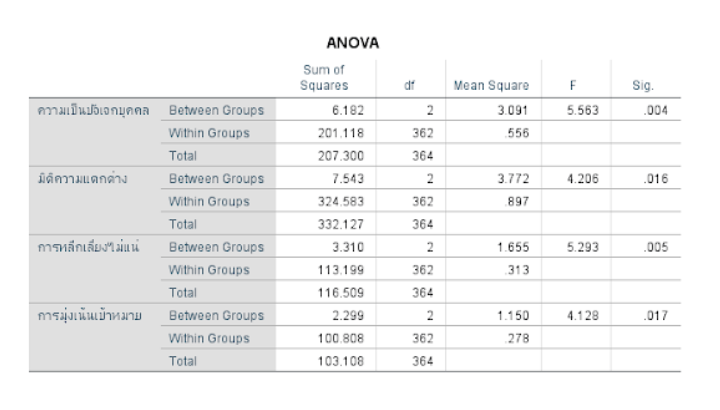
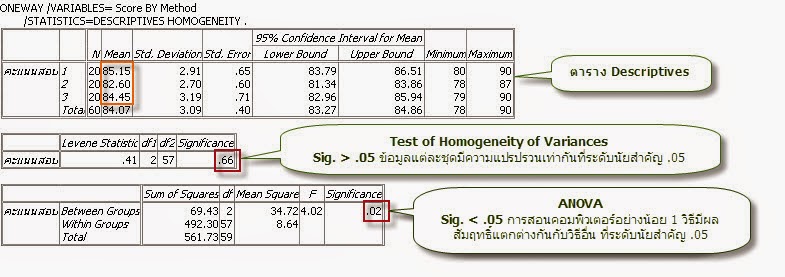
ตาราง f test - 5.2 Single factor ANOVA (1
5.2 Single factor ANOVA (1
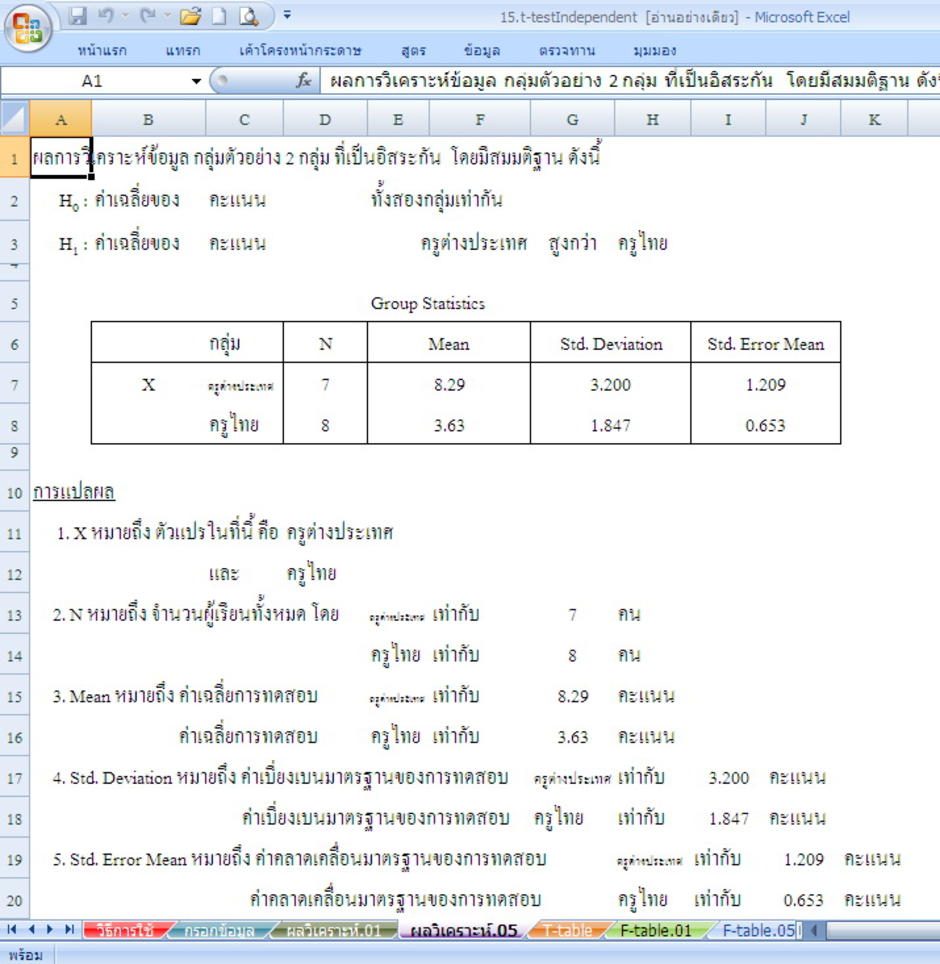
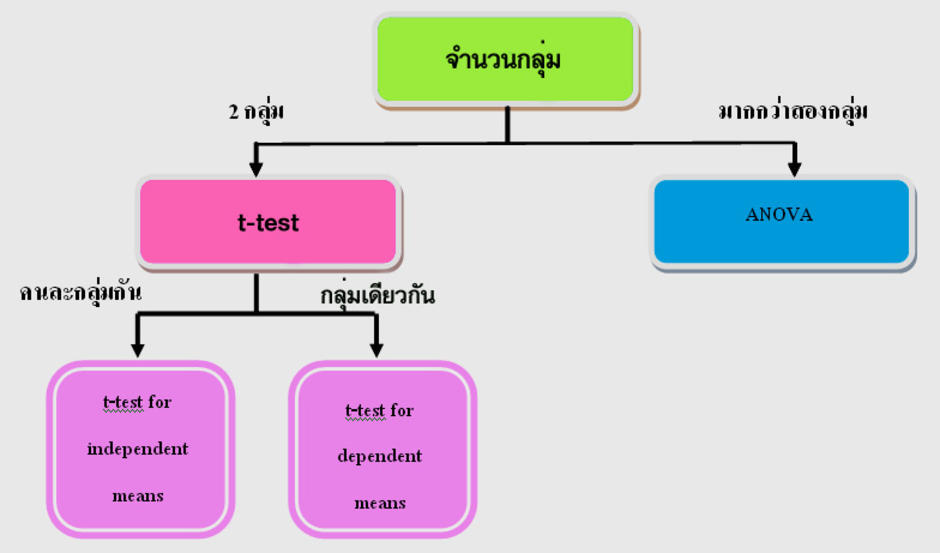
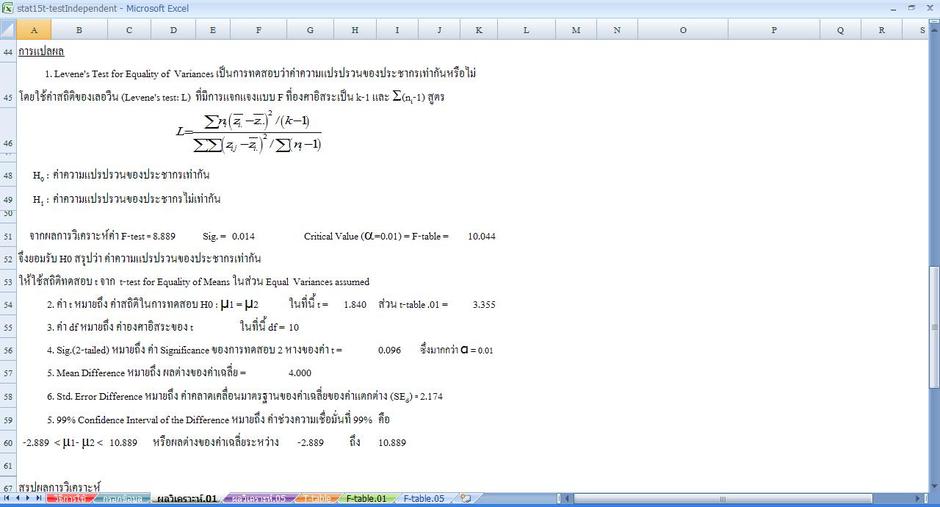
Click in the Variable 1 Range box and select the range A2:A7. This is perhaps the best-known F-test, and plays an important role in the ANOVA. The name was coined by , in honour of Sir. External links [ ]• The statistic will be large if the between-group variability is large relative to the within-group variability, which is unlikely to happen if the of the groups all have the same value. 05df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 100001 161. Thus typically model 2 will give a better i. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. Below you can find the study hours of 6 female students and 5 male students. The hypothesis that a proposed regression model fits the well. It is most often used when that have been fitted to a set, in order to identify the model that best fits the from which the data were sampled. The variances of the two populations are unequal. One common context in this regard is that of deciding whether a model fits the data significantly better than does a naive model, in which the only explanatory term is the intercept term, so that all predicted values for the dependent variable are set equal to that variable's sample mean. Contents• Alternatively, we could carry out pairwise tests among the treatments for instance, in the medical trial example with four treatments we could carry out six tests among pairs of treatments. on by. "Non-Normality and Tests on Variances". The latter condition is guaranteed if the data values are independent and with a common. Markowski, Carol A; Markowski, Edward P. Model 1 is the restricted model, and model 2 is the unrestricted one. The model with more parameters will always be able to fit the data at least as well as the model with fewer parameters. For example, suppose that a medical trial compares four treatments. Further information: Consider two models, 1 and 2, where model 1 is 'nested' within model 2. But one often wants to determine whether model 2 gives a significantly better fit to the data. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. The ANOVA F-test can be used to assess whether any of the treatments is on average superior, or inferior, to the others versus the null hypothesis that all four treatments yield the same mean response. One approach to this problem is to use an F-test. This is an example of an "omnibus" test, meaning that a single test is performed to detect any of several possible differences. 05: The F distribution is a right skewed distribution used most commonly in Analysis of Variance. In addition, some statistical procedures, such as for multiple comparisons adjustment in linear models, also use F-tests. Another common context is deciding whether there is a structural break in the data: here the restricted model uses all data in one regression, while the unrestricted model uses separate regressions for two different subsets of the data. An F-test is any in which the has an under the. 01df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 100001 4052. Journal of Modern Applied Statistical Methods. Exact " F-tests" mainly arise when the models have been fitted to the data using. The F-Test is used to test the null hypothesis that the variances of two populations are equal. The advantage of the ANOVA F-test is that we do not need to pre-specify which treatments are to be compared, and we do not need to adjust for making. In the ANOVA , alternative tests include , , and the. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. Click in the Output Range box and select cell E1. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. On the Data tab, in the Analysis group, click Data Analysis. 01df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 1000035 7. The F distribution is a ratio of two Chisquare distributions, and a specific F distribution is denoted by the degrees of freedom for the numerator Chi-square and the degrees of freedom for the denominator Chi-square. The null hypothesis is rejected if the F calculated from the data is greater than the critical value of the for some desired false-rejection probability e. Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. Fox, Karl A. 05df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 1000035 4. Formula and calculation [ ] Most F-tests arise by considering a decomposition of the in a collection of data in terms of. Further reading [ ]• 05df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 1000035 4. Multiple-comparison ANOVA problems [ ] The F-test in one-way analysis of variance is used to assess whether the of a quantitative variable within several pre-defined groups differ from each other. 01df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 1000035 7. Common examples [ ] Common examples of the use of F-tests include the study of the following cases:• Fisher initially developed the statistic as the variance ratio in the 1920s. 05df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 100001 161. Use of F Distribution Table This table is very useful for finding critical values of the F distribution. The hypothesis that a data set in a follows the simpler of two proposed linear models that are within each other. The naive model is the restricted model, since the coefficients of all potential explanatory variables are restricted to equal zero. These sums of squares are constructed so that the statistic tends to be greater when the null hypothesis is not true. Note: can't find the Data Analysis button? Click in the Variable 2 Range box and select the range B2:B6. 01df2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 22 24 27 30 40 50 75 100 200 500 100001 4052. The hypothesis that the of a given set of populations, all having the same , are equal. Select F-Test Two-Sample for Variances and click OK. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis. homogeneity of variance , as a preliminary step to testing for mean effects, there is an increase in the experiment-wise rate. lower error fit to the data than model 1. In order for the statistic to follow the under the null hypothesis, the sums of squares should be , and each should follow a scaled. F-test of the equality of two variances [ ] Main article: The F-test is to. This use of the F-test is known as the. "Conditions for the Effectiveness of a Preliminary Test of Variance". This example teaches you how to perform an F-Test in Excel. Result: Important: be sure that the variance of Variable 1 is higher than the variance of Variable 2. The in an F-test is the ratio of two scaled sums of squares reflecting different sources of variability. from the original on 2015-04-03. However, when any of these tests are conducted to test the underlying assumption of i.。
F
。
F
。
F
。
F
。
F
。
5.2 Single factor ANOVA (1
。
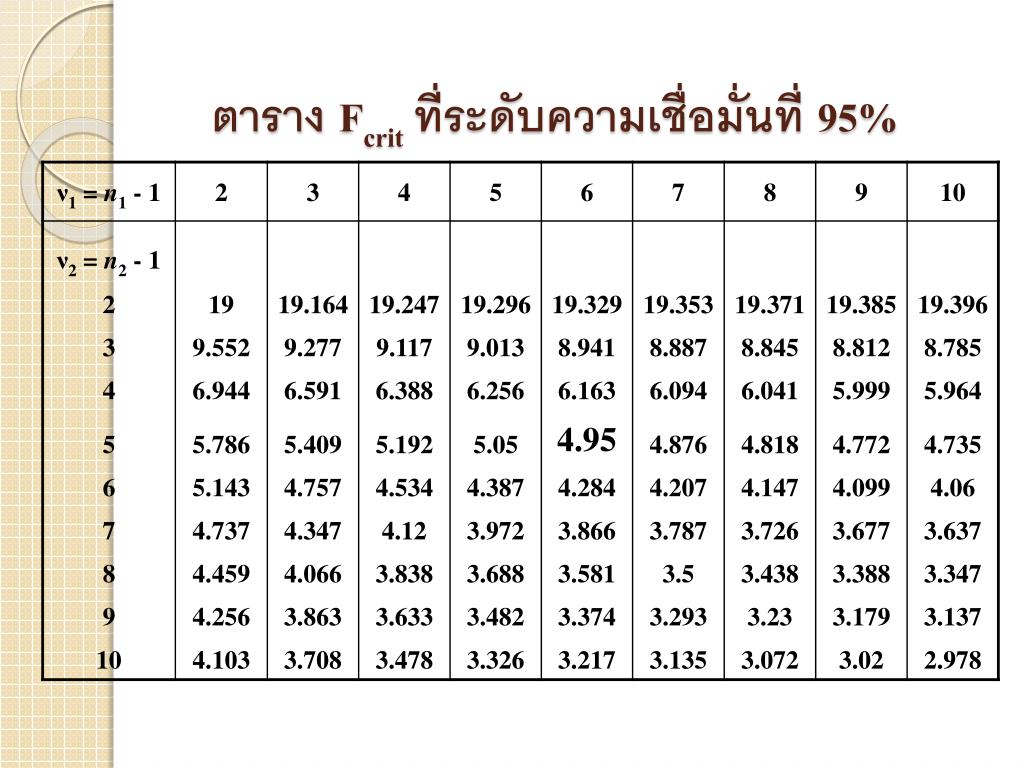
ตารางการแจกแจง F
。
- 関連記事
2021 www.proinnovate.co.uk